

The peripheral nervous system also controls the release of secretions from most exocrine glands. It is necessary for all voluntary action, balance, and maintenance of posture. It can increase or decrease the strength of muscle contractility across the body, whether it is sphincters in the digestive and excretory systems, cardiac muscles in the heart, or skeletal muscles for movement. Thus, the PNS regulates internal homeostasis through the autonomic nervous system, modulating respiration, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion reproduction, and immune responses. When the CNS integrates these varied signals and formulates a response, motor nerves of the PNS innervate effector organs and mediate the contraction or relaxation of skeletal, smooth or cardiac muscle. This is accomplished through nerves that carry information from sensory receptors in the eyes, ears, skin, nose, and tongue, as well as stretch receptors and nociceptors in muscles, glands and other internal organs. The primary function of the peripheral nervous system is to connect the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body and the external environment.
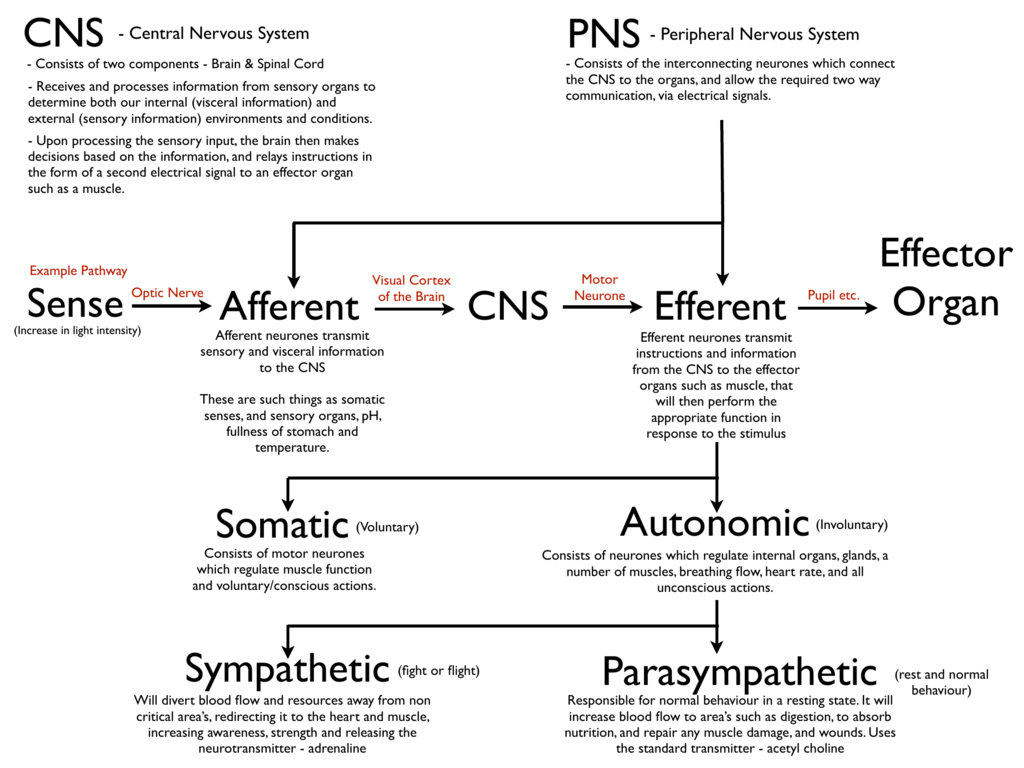
While it receives signals from the autonomic nervous system, it can function independently and contains nearly five times as many neurons as the spinal cord. The enteric nervous system, which surrounds the gastrointestinal tract, is another important part of the peripheral nervous system. Both cranial and spinal nerves can have sensory, motor, or mixed functions. Anatomically, the PNS can be divided into spinal and cranial nerves, depending on whether they emerge from the spinal cord or the brain and brainstem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
